Analyzing the Effectiveness of Abandoned Cart Recovery Strategies in Boosting Online Sales

The eCommerce world is filled with opportunities—and challenges. One of the most significant issues online retailers face is the abandoned shopping cart. Studies show that up to 70% of online shopping carts are abandoned before checkout. For businesses, that’s a substantial amount of potential revenue slipping away. This is where abandoned cart recovery strategies come into play, helping brands bring back lost customers and boost online sales.
In this blog, we’ll dive into the most effective strategies for recovering abandoned carts, how to measure their success, and what metrics you should be tracking.
Email remarketing is one of the most widely used strategies to recover abandoned carts. It involves sending targeted emails to customers who added items to their cart but left without completing their purchase. These emails often include reminders, product images, and even discounts to encourage customers to come back and finish their orders.
Why does it work?Abandoned cart recovery emails are effective because they act as a gentle nudge to shoppers who might have been distracted or undecided. Personalization and timing are key—emails sent within an hour of cart abandonment tend to perform best.
Success Data:- The average open rate for abandoned cart emails is around 45%, and click-through rates hover around 21%.
- Businesses see an average abandoned cart recovery rate of 10–15% through email campaigns.


Retargeting ads are online advertisements specifically shown to users who have previously visited your website or added items to their shopping cart. These ads appear across social media platforms or on other websites the shopper visits, reminding them of their abandoned items.
Why does it work?Retargeting keeps your brand and products top of mind for potential customers. Sometimes, all a shopper needs is a visual reminder of what they left behind to return and make a purchase.
Success Data:- Retargeting ads can increase conversion rates by 20–30%.
- Businesses report seeing a 4–6x return on ad spend (ROAS) from effective retargeting campaigns.
Cart recovery pop-ups are real-time notifications or messages that appear when a customer is about to leave your website without completing their purchase. These pop-ups can offer discounts, highlight free shipping, or even display a sense of urgency, such as “Only 2 items left in stock!”
Why does it work?These pop-ups work by addressing the customer’s hesitation at the moment it occurs. Whether it’s offering a solution to high shipping costs or a reminder of limited stock, they tackle objections head-on.
Success Data:- Well-designed pop-ups can recover up to 15% of abandoned carts.
- Conversion rates from cart recovery pop-ups typically range from 5–8%.

Incentives like discounts, free shipping, or bonus items can entice customers to return and complete their purchase. These incentives are often presented through email campaigns, pop ups, or SMS messages.
Why does it work?Price is one of the top reasons for cart abandonment. Offering a small discount or free shipping can make a big difference, especially for price-sensitive customers.
Success Data:- Incentives can boost cart recovery rates by 10–20%.
- Customers who receive a discount are more likely to make repeat purchases, increasing their lifetime value.
Measuring the Success of Recovery Strategies
Implementing abandoned cart recovery strategies is just the first step. To truly understand their effectiveness, you need to measure key metrics and track specific KPIs. Here’s what you should focus on:
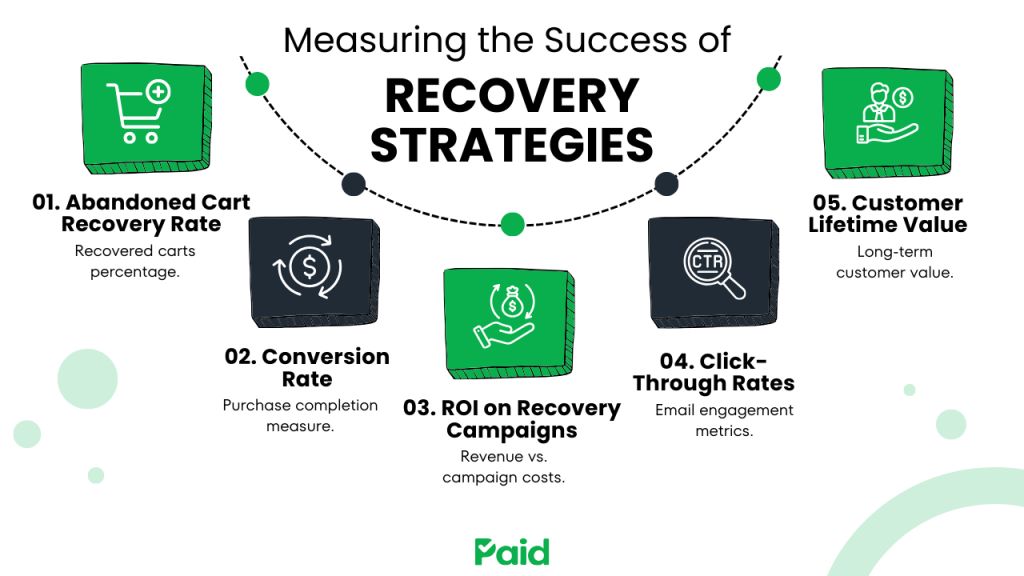
This is the percentage of abandoned carts that are successfully recovered. A good abandoned cart recovery rate is typically around 10–20%, depending on the strategy used.
How to calculate it:
Abandoned Cart Recovery Rate = (Recovered Carts/Total Abandoned Carts) × 100
2. Conversion RateTrack how many users complete their purchase after interacting with your recovery strategy, such as opening an email, clicking on a retargeting ad, or engaging with a pop-up.
3. ROI on Recovery CampaignsCalculate the revenue generated from your cart recovery efforts compared to the cost of implementing those strategies.
4. Email Open and Click-Through RatesFor email remarketing campaigns, monitor the percentage of recipients who open the email and click through to your website. These metrics help you gauge the effectiveness of your email content and timing.
5. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)If your recovery strategies include offering incentives, track whether these customers make repeat purchases. This helps measure the long-term impact of your efforts.
Case Study: How a merchant boosted Abandoned Cart Recovery Rate by 30%
Abandoned carts are a persistent challenge for eCommerce businesses, often leaving a significant amount of revenue untapped. One major retailer on paid.com decided to tackle this problem by implementing a robust abandoned cart recovery strategy. Their results? A recovery rate that surged to 30%—well above the industry average. Here’s how they did it.
The ChallengeThis eCommerce retailer struggled with a high cart abandonment rate, which meant potential customers were leaving without completing their purchases.
The SolutionThe business introduced an abandoned cart recovery workflow that combined timely follow-ups and attractive incentives:

The first recovery email was sent just 15 minutes after cart abandonment, reminding customers of their items while the intent was still fresh.
The emails were tailored to include the customer’s name and the specific items in their cart.

To encourage action, the first email included a 10% discount valid for a limited time, creating urgency.
Over the following months, their recovery rate climbed steadily, reaching an impressive 26%. After further refinements and consistent testing, including tweaking email subject lines and discount amounts, the company achieved a 30% abandoned cart recovery rate.
What’s Next?Despite the success, the retailer recognized that there was still room for growth. To further improve, they planned to:
- Implement retargeting ads on social media to reach customers who ignored emails.
- Introduce SMS reminders for more immediate engagement.
- Use advanced AI to analyze customer behavior and optimize the timing and content of recovery efforts.
This case study shows that a well-timed and personalized abandoned cart recovery workflow can significantly boost recovery rates. By continually testing and optimizing their strategy, this retailer turned abandoned carts into a major revenue source.
PAID: A Comprehensive Platform for Business Growth
PAID is a powerful platform designed to help businesses streamline their operations, from creating high-converting websites to managing payments and customer engagement. It caters to businesses of all sizes, offering tools that are user-friendly and effective for driving growth.
Backed by WebOsmotic, a leader in IT solutions, PAID integrates essential business functionalities, including abandoned cart recovery, secure payments, and invoicing, into a seamless experience. Every aspect of the platform is designed to empower business owners to create websites that convert, engage, and grow their audience effectively.
Conclusion
Reach out to WebOsmotic for innovative custom AI solutions, Web and Mobile App Development, UI-UX Design and more.

